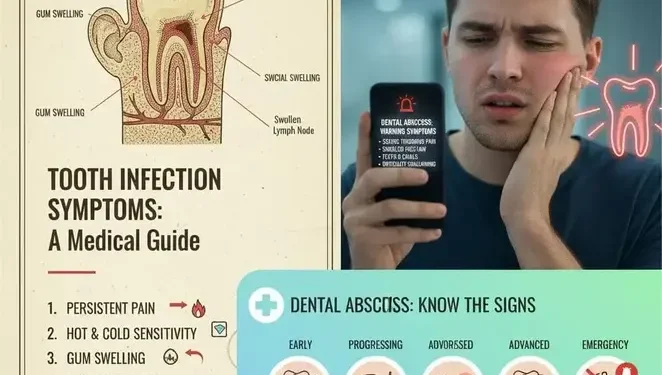
A tooth infection rarely starts with drama. It usually begins with a mild ache that feels easy to ignore. Many people assume it will settle down on its own. But that assumption causes problems.
A tooth infection does not behave like a common headache. It grows quietly, builds pressure, and waits for an opportunity to spread. Recognising the symptoms early can prevent serious complications and, in rare cases, save your life.
A tooth infection may cause persistent pain, swelling, bad taste, fever, or facial swelling. Early treatment prevents serious and potentially life threatening complications.
This article will explain how to know if you have a tooth infection, what symptoms matter most, and when a “simple toothache” becomes a medical issue.
What Is a Tooth Infection?
A tooth infection, often called a dental abscess, occurs when bacteria enter the inner part of a tooth. This inner area, known as the pulp, contains nerves and blood vessels.
Once bacteria reach the pulp:
- The tooth becomes inflamed
- Pus begins to form
- Pressure builds inside the tooth
The infection cannot drain naturally. Without treatment, it spreads.
Common causes include:
- Untreated cavities
- Cracked or broken teeth
- Gum disease
- Failed fillings or crowns
Early Symptoms of a Tooth Infection
Early symptoms often feel manageable. That is why many people delay treatment.
Persistent Tooth Pain
This pain:
- Feels deep and throbbing
- Does not fully go away
- Often worsens at night
Painkillers may reduce it, but relief rarely lasts.
Sensitivity to Hot or Cold
Lingering pain after hot or cold foods suggests nerve involvement. If the pain stays for more than a few seconds, infection may already be present.
Pressure Pain While Chewing
If biting down causes sharp pain, inflammation inside the tooth may increase.
Mild Gum Swelling
You may notice:
- Redness near one tooth
- Tender or puffy gums
This swelling often looks harmless but signals infection beneath the surface.
Signs the Infection Is Getting Worse
As bacteria multiply, symptoms become harder to ignore.
Throbbing, Radiating Pain
Pain may spread to:
- Jaw
- Ear
- Neck
- Side of the face
This usually means the infection has reached surrounding tissues.
Gum Boil or Pimple
A small bump on the gums that:
- Looks like a pimple
- Leaks pus or fluid
- Tastes bitter
This is a classic sign of an abscess trying to drain.
Bad Taste or Persistent Bad Breath
Pus drainage leaves a foul taste. Mouthwash may mask it briefly, but it returns.
Fever and Fatigue
A fever shows your body is fighting infection. Feeling unusually tired often accompanies it.
Advanced and Dangerous Symptoms
These symptoms require urgent dental or medical care.
Facial or Jaw Swelling
Swelling that affects:
- Cheeks
- Lips
- Jawline
means infection has moved beyond the tooth.
Difficulty Swallowing or Breathing
This may signal infection spreading toward the throat or airway. This is a medical emergency.
Swollen Lymph Nodes
Tender lumps under the jaw or in the neck suggest systemic involvement.
Confusion or Dizziness
These symptoms can indicate infection entering the bloodstream.
If you experience any of these, do not wait for a dental appointment; rather, rush for emergency care.
Does Pain Always Mean Infection?
Not always, but absence of pain does not mean safety either.
Some infections kill the tooth nerve. When the nerve dies:
- Pain suddenly stops
- The infection continues silently
This stage often fools people into thinking the problem is resolved, but in fact, it is not.
Silence can be dangerous.
Tooth Infection vs Regular Toothache
Not all tooth pain signals infection.
Regular Toothache
- Comes and goes
- Improves with pain relief
- Often linked to sensitivity
Tooth Infection
- Persistent or worsening pain
- Swelling or pus
- Fever or fatigue
- Bad taste or odor
If symptoms last more than two days, infection becomes more likely.
How Dentists Diagnose Tooth Infections
Dentists use:
- Dental X-rays to detect abscesses
- Physical examination
- Sensitivity and pressure testing
X-rays often reveal infection before it causes severe pain.
Early diagnosis simplifies treatment and reduces risk.
Why You Should Never Ignore These Symptoms
Ignoring tooth infection symptoms can lead to:
- Bone damage
- Spread to sinuses or neck
- Blood infection (sepsis)
- Hospitalization
- Severe cases can become life-threatening if untreated.
- Most complications occur because people wait too long.
What To Do If You Suspect a Tooth Infection
Step 1: Contact a Dentist Immediately
Even if pain seems manageable, infection rarely resolves without treatment.
Step 2: Avoid Home “Fixes”
Clove oil, garlic, or aspirin on the tooth do not treat infection. They may worsen irritation.
Step 3: Follow Professional Treatment
Treatment may include:
- Root canal therapy
- Abscess drainage
- Tooth extraction
- Antibiotics as support
Antibiotics alone do not cure dental abscesses.
When to See a Dentist Immediately for a Tooth Infection
Seek urgent medical or dental care if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Facial, jaw, or neck swelling, especially if it is rapidly increasing
- Fever with worsening tooth pain, fatigue, or general illness
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing, which may indicate airway involvement
- Persistent pus discharge, severe pain, or swollen lymph nodes
Delaying treatment at this stage increases the risk of infection spreading beyond the tooth and becoming a medical emergency.
Can Tooth Infections Heal on Their Own?
The answer to this question is no. The body cannot fully eliminate an abscessed tooth infection without dental intervention. Symptoms may pause, but bacteria remain active.
Delayed treatment increases:
- Cost
- Pain
- Risk
Early care protects your health and wallet.
Prevention: Stop Infection Before It Starts
Prevention remains simple and effective.
- Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
- Floss once a day
- Treat cavities early
- Get dental checkups every 6–12 months
Routine care prevents most abscesses.
Remember, skipping appointments saves time today and costs health later.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How do I know if I have a tooth infection?
Common signs include persistent tooth pain, swelling, fever, bad taste, and sensitivity. A dentist confirms infection with an examination and X-rays.
2. Can a tooth infection go away without treatment?
No. Pain may fade, but the infection remains. Untreated infections often worsen over time.
3. Is tooth infection an emergency?
It becomes an emergency if you have facial swelling, fever, or difficulty breathing, or swallowing. These signs require immediate care.
4. Can antibiotics cure tooth infection?
Antibiotics help to spread but do not remove the infected tissue. Dental treatment is necessary.
5. What happens if a tooth infection spreads?
It may spread to the jaw, neck, bloodstream, or brain. This can cause serious complications like sepsis.
6. Does tooth infection always hurt?
No. Pain may disappear if the nerve dies. Infection can still spread silently.
7. How fast can symptoms worsen?
In some cases, symptoms worsen within days. Progression depends on immunity, location, and treatment delay.
Final Thoughts
Tooth infections do not announce themselves loudly at first. They whisper, wait, and spread.
Recognising symptoms early makes treatment simple. Ignoring them makes treatment complex and risky. If your body sends signals of pain, swelling, and fever, listen.